Project Profile: Shandong Coking Co., Ltd. is located in a city in Shandong Province. With the development of domestic economy, it has reached an annual output of 420,000 tons of high-quality coke, 18,000 tons of processed tar and 3,900 tons of crude benzene. It has formed a complete industrial chain integrating coal washing, coking, tar recovery and processing, storage and transportation. As the company continues to grow, so does the emphasis on environmental protection. The company listed wastewater reuse in its recent development plan, which shows its emphasis on wastewater treatment and reuse. The company was entrusted by Party A to conduct a detailed and thorough investigation of the internal and external environment of the whole plant. Based on the advanced technology and experience of coking wastewater treatment and reuse at home and abroad, the company formulated and designed the 1000 tons/day wastewater treatment project of the company.
The company's 1,000 tons / day wastewater treatment project, the design of integrated wastewater influent water quality is as follows:
|
Name |
Unit |
Index value |
|
CODcr |
mg/l |
≤2600 |
|
BOD5 |
mg/l |
≤1000 |
|
pH |
- |
7-8 |
|
SS |
mg/l |
≤210 |
|
Cyanide |
mg/l |
≤8 |
|
NH3-N |
mg/l |
≤150 |
|
oil |
mg/l |
≤200 |
|
Volatile phenol |
mg/l |
≤600 |
After the wastewater is treated, it is superior to the first-class standard of the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB8978-1996). The specific indicators of the standard are as follows:
|
Name |
Unit |
Index value |
|
CODcr |
mg/l |
≤100 |
|
BOD5 |
mg/l |
≤20 |
|
pH |
- |
6-9 |
|
SS |
mg/l |
≤70 |
|
Cyanide |
mg/l |
≤0.5 |
|
NH3-N |
mg/l |
≤15 |
|
oil |
mg/l |
≤10 |
|
Volatile phenol |
mg/l |
≤0.5 |
Project process:
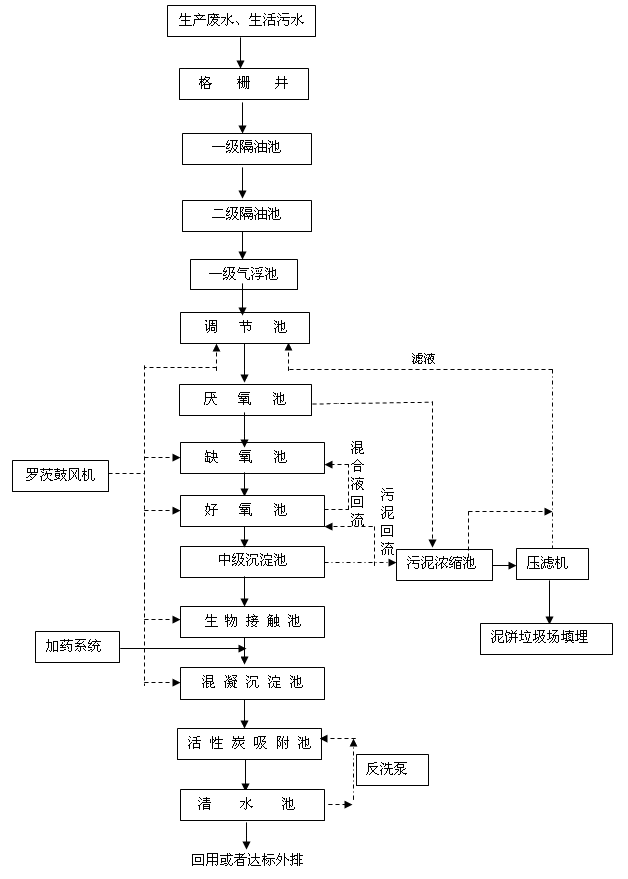
Project process description:
The production wastewater and domestic sewage in the plant area are collected through the pipe network of the plant to collect the large pieces of vegetables and fruit residues from the fine grid well, and then into the two-stage grease trap to remove the oil beads and parts with larger particle size in the raw water. The heavier impurities, the waste water passing through the grease trap enters the air floatation tank, and the demulsifier, the coagulant and the floc aid are added. The emulsified tar can be effectively removed, and the CODcr and BOD5 are also partially removed. The normal biochemical treatment is guaranteed. The wastewater after air flotation enters the regulating tank, and a perforated aeration pipe is arranged in the regulating tank to adjust the amount of wastewater and the water quality.
The water in the conditioning tank is driven into the anaerobic tank by the submersible pump. Anaerobic microorganisms have a metabolic process different from that of aerobic microorganisms for the cleavage of a heterocyclic compound and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring, which is cleaved into a reductive cleavage and a non-reductive cleavage. The main purpose of the anaerobic biological fermentation tank is to remove CODcr and improve the biodegradability of the wastewater. Anaerobic process For organic wastewater with a high concentration, the organic matter in the wastewater can be decomposed into methane and the like, and discharged from the pool in the form of gas. At the same time, it is also possible to open the rings of benzene, naphthalene and anthracene in the aromatic hydrocarbon organic matter in the wastewater, thereby improving the aerobic biodegradability of the refractory organic matter, and creating favorable conditions for the subsequent aerobic biological treatment.
The effluent from the anaerobic tank flows into the anoxic tank, which is the main structure of biological nitrogen removal. The NH3-N in the wastewater is converted into a nitrifying mixture of NO3--N and NO2--N by the nitrifying and nitrosating bacteria in the next-stage aerobic nitrification tank, and is recycled to the anoxic tank and passed through the biological reduction of the denitrifying bacteria. Role, NO3--N and NO2--N are converted to N2. The sewage from the anoxic tank flows into the aerobic tank and flows into the push-flow activated sludge aeration tank to complete the nitrification process of the ammonia-containing wastewater. Nitrifying bacteria are autotrophic aerobic bacteria. Under aerobic conditions, NH3-N in wastewater is oxidized to NO3--N, and organic pollutants are better degraded under the action of aerobic bacteria.
The wastewater in the aerobic tank flows into the secondary settling tank, so that the activated sludge and other particulate matter in the water can be separated in the pool, and a part of the sludge is returned to the aerobic tank to increase the sludge age in the pool, and promote the nitrification reaction in the pool, and another part of the sewage The mud is discharged into the sludge concentration tank to achieve the purpose of removing phosphorus and some organic matter.
he wastewater separated by mud water flows into the biological contact oxidation tank, and the wastewater is in contact with the microorganisms on the filler in the pool, and the organic matter in the water is adsorbed by the microorganisms and oxidized and decomposed to purify the wastewater. The aerobic tank sewage is subjected to a coagulation reaction to further remove suspended solids, colloids and partially non-soluble organic matter in the water. The sewage after the coagulation reaction is again separated into the activated carbon filter by the mud water separation, and the pollutants in the effluent of the coagulation sedimentation tank are finally treated by the adsorption and filtration action of the activated carbon in the activated carbon filter. Ensure that the effluent can be used for reuse and compliance of the plant.
Project Project Picture: Biochemical Pool in Operation


Scan It