Project Description: Jiangsu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. mainly produces seven kinds of antibiotics: cefminox sodium, cefuroxime sodium, meadazole acid, cefoxitin sodium, cefathiamidine, ceftime monosodium, cefpirome sulfate. The sewage generated in the production process mainly includes process discharge sewage, domestic sewage, water ring pump discharge sewage, boiler steam drainage and pure water preparation wastewater. The process discharge sewage concentrated water has the characteristics of chlorine, ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus, contains a certain amount of sulfate and has certain bactericidal properties due to the characteristics of the added materials and products. The wastewater is generally acidic, with high CODcr concentration, high salt content and poor biodegradability. The amount of wastewater in this type of wastewater is about 160 tons/day, and the fresh water discharged from the process is about 170 tons/day. The amount of water discharged from domestic sewage, water ring pump, and boiler steam drainage is about 800 tons/day. The CODcr of these types of wastewater is 400mg/ l Relatively low pollutants, better treatment. This design sewage treatment system 1200 tons / day wastewater treatment project.
The wastewater indicators of each section are as follows:
| Drainage source | Water quantity (ton / day) | COD (mg/L) | pH | Salt (mg/L) | Sulfate (mg/L) | Total nitrogen (mg/L) | Total phosphorus (mg/L) | Chloride ion (mg/L) |
| Process concentrated sewage | 160 | 85000 | 2.1 | 83000 | 1900 | 1382 | 220 | 8910 |
| Process fresh sewage | 170 | 4500 | 7 | 5000 | 110 | 50 | 5 | 790 |
| domestic sewage | 100 | 300 | 7 | 45 | 5 | |||
| Water ring pump drainage | 500 | 400 | 7 | |||||
| Other drainage | 200 | 200 | 7 | |||||
| Total | 1130 | 12570 | 6.2 | 15346 | 357.1 | 250.4 | 42 | 1567 |
处理后的污水接入城市污水处理厂,执行国家《污水综合排放标准》(GB8978-1996)中的第二类污染物的三级排放标准及当地接入污水厂的进水控制要求根据业主提供的资料,排放标准为接纳污水厂的接受标准:
| Content | COD (mg/L) | pH | BOD | TN (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
| (mg/L) | ||||||
| Emission Standards | ≤500 | June 9 | ≤300 | ≤100 | ≤35 | ≤5 |
Introduction to the project process:
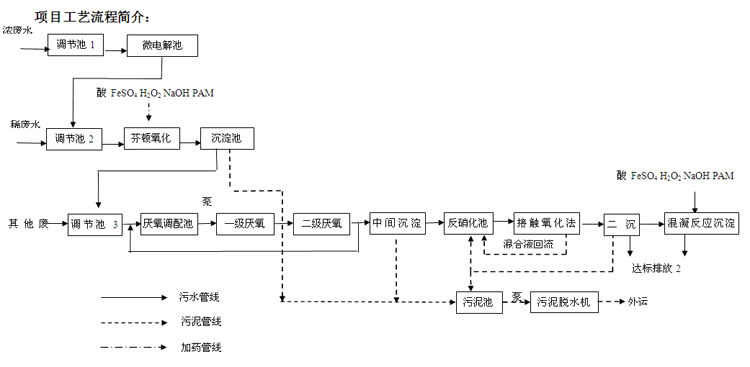
Project process description:
The production wastewater in the plant area is collected through the pipe network, which is mainly divided into the production of concentrated water, production of fresh water, and other miscellaneous water. The concentrated wastewater is produced into the regulating tank 1, and is pumped to the micro-electrolysis cell to reduce the toxicity of the wastewater and improve the biodegradability of the wastewater through micro-electrolysis. The production of dilute wastewater and the treated concentrated wastewater are mixed into the conditioning tank 2, and are pumped to the Fenton reaction sedimentation tank. The strong oxidizing action of Fenton's reagent is used to oxidize the hardly biodegradable macromolecular substance into small molecular substances, thereby improving The biochemical property of the wastewater, the effluent after oxidation is added to the flocculant to remove most of the colloidal substances and some organic matter. The pre-processed production of concentrated/dilute wastewater is mixed with other wastewater into the regulating tank 3, and the water quality and water quantity are adjusted for all the wastewater to ensure the stability of subsequent treatment.
Regulating the effluent of the pool 3 into the anaerobic mixing tank, in order to improve the biochemical treatment effect, meet the requirements of the balanced nutrition of the microorganisms, and provide a suitable growth environment for the microorganisms to increase the nutrient salt containing nitrogen and phosphorus in the intermediate pool (according to the actual water supply situation, the debugging is determined) At the same time, the heating device is arranged to heat the wastewater when the water temperature is low in winter, so that the temperature of the wastewater is not lower than 30 °C.
The effluent of the dosing tank is pumped to the first-stage anaerobic reactor, and a thermometer is set in the anaerobic tank to observe the temperature change. Most of the organic matter in the wastewater in the anaerobic tank is decomposed into carbon dioxide, methane and other gases by the action of anaerobic bacteria, and a small amount of organic matter is absorbed by the microorganism to synthesize its own substance. The excess sludge per day can be regularly removed from the bottom sludge pipe. A three-phase separator is arranged in the upper part of the anaerobic tank to effectively separate the gas, the sludge and the water, and the effluent flows into the intermediate sedimentation tank, and a part of the effluent from the sedimentation tank is returned to the mixing tank in the preceding stage to reduce the organic pollution load of the influent, and the rest Enter the biochemical reaction pool. The biogas generated during the anaerobic reaction process is collected into a water-sealed tank and adjusted accordingly, and then directly burned by a torch or comprehensively utilized according to actual conditions.
The effluent from the intermediate pond flows into the denitrification tank, and the nitrate nitrogen is removed by the action of denitrifying bacteria. The effluent enters the contact oxidation pond, and the organic matter in the wastewater is further degraded by the action of aerobic bacteria, and the ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater is also oxidized. The nitrate nitrogen is returned to the denitrification tank through the mixed liquid, and an on-line dissolved oxygen meter is arranged in the contact oxidation tank, and the amount of aeration can be controlled by the change of dissolved oxygen. After the contact oxidation pond is provided with a secondary settling tank, the excess sludge can be discharged into the sludge tank by the secondary sedimentation tank, and part of the sludge is returned to the aerobic tank.
The sludge of the whole sewage treatment system mainly comes from the excess sludge such as Fenton oxidation sedimentation tank, anaerobic sedimentation tank and biochemical sedimentation tank. The sludge generated by the system is discharged to the sludge tank by gravity or pump, and is transported by the sludge pump to the plate and frame dewatering machine to complete the dewatering and volume reduction treatment, and finally the external transportation is carried out for comprehensive solid waste treatment.
In addition, the processing station also has auxiliary processing facilities such as the drug preparation and dosing area to ensure that the water in the fluctuation of water quality can still be discharged to a stable level.
Project Project Picture: Micro-electrolysis equipment and biochemical pool in operation



Scan It