Project Description: A small island is one of the 13 severely water-deficient islands in Zhoushan City. The island has about 5,000 residents. Due to the constraints of geography and terrain, the development of freshwater resources is very difficult. In normal times, the whole island is available for fresh water of 160,000 tons, water demand is about 230,000 tons, and water shortage is 70,000 tons per month. In view of the fact that the water source cannot meet the improvement of the domestic living water and the development of the industry, it is necessary to increase the water source and develop stable and reliable fresh water resources. Our company combines local characteristics with its own desalination technology to provide the following technical design.
The design inlet water quality is as follows:
| Serial number | Project | Unit | Average value | Range |
| 1 | pH | 7.93 | 7.29~8.38 | |
| 2 | M-alkalinity | mmol/l | 2.44 | 2.2~2.5 |
| 3 | hardness | mmol/l | 126.7 | 115~139 |
| 4 | Ca2+ | mmol/l | 22.8 | 18.5~25.5 |
| 5 | Mg2+ | mmol/l | 103.8 | 96.25~118 |
| 6 | Fe3+ | mg/l | 0.09 | 0.08~0.14 |
| 6 | Na+ | mg/l | 10763 | 9270~13187 |
| 7 | CI- | mg/l | 18300 | 17300~19400 |
| 8 | SO42- | mg/l | 2567.7 | 2430~3014 |
| 9 | H2S | mg/l | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | active silicon | mg/l | 0.93 | 0.42~1.78 |
| 11 | COD | mg/l | 8.12 | 4.8~10 |
| 12 | suspended matter | mg/l | 147.4 | 64.7~178.8 |
| 13 | Dissolved solids | mg/l | 33692.7 | 31277.3~36937.3 |
Design the water quality:
For living drinking water, system output of 300 tons / day (25 ° C), the first-level RO system recovery rate of 35%. The salt rejection rate is 60%, the secondary RO system recovery rate is 70%, and the salt rejection rate is 85%.
Introduction to the project process:
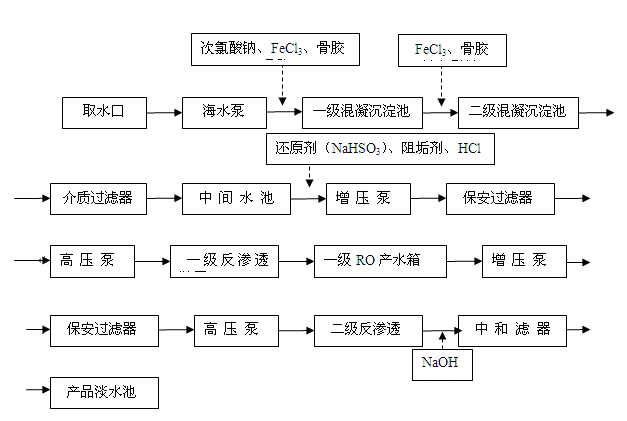
Introduction to the project process:
According to the surrounding environment around the seawater desalination plant, the available site adopts a feasible water intake method, and the water intake port is provided with a grid to intercept impurities, and the water intake is located at a sea level of 2 m to ensure continuous supply of seawater. The seawater pump raises the seawater into the first-stage coagulation tank. The coagulation tank is used to kill algae and bacteria by adding sodium hypochlorite. At the same time, FeCl3 is added as a coagulant, and the bone cement is used as a coagulant to carry out the coagulation reaction to remove the suspension in the seawater. Material, colloid, turbidity, color, etc., the water in the first-stage coagulation sedimentation tank flows into the secondary coagulation tank for secondary coagulation reaction, further removes the above substances, and the effluent flows into the medium filter, the medium filter The separation and removal of the suspended solids in the coagulation sedimentation tank are not separated, the turbidity is lowered, and the like. The medium filter effluent flows into the middle pool, and the water in the middle pool is pressurized by the booster pump through the security filter, and is pumped into the first-stage RO system through the high-pressure pump, and the reducing agent (NaHSO3) is added before the booster pump to inhibit the scale. The agent and the HCl agent reduce the excessive oxidant in the water by NaHSO3, and at the same time, the scale inhibitor is added to prevent the insoluble salts such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and calcium sulfate in the reverse osmosis concentrated water from being concentrated to precipitate scale and block the RO membrane. The RO system generates the water into the first-level RO water tank. The first-stage RO water is pumped into the secondary RO system through the booster pump, the security filter, and the high-pressure pump. The water is added to the NaOH to adjust the pH to neutral and finally enter the product freshwater pool.
Project project picture:


Scan It